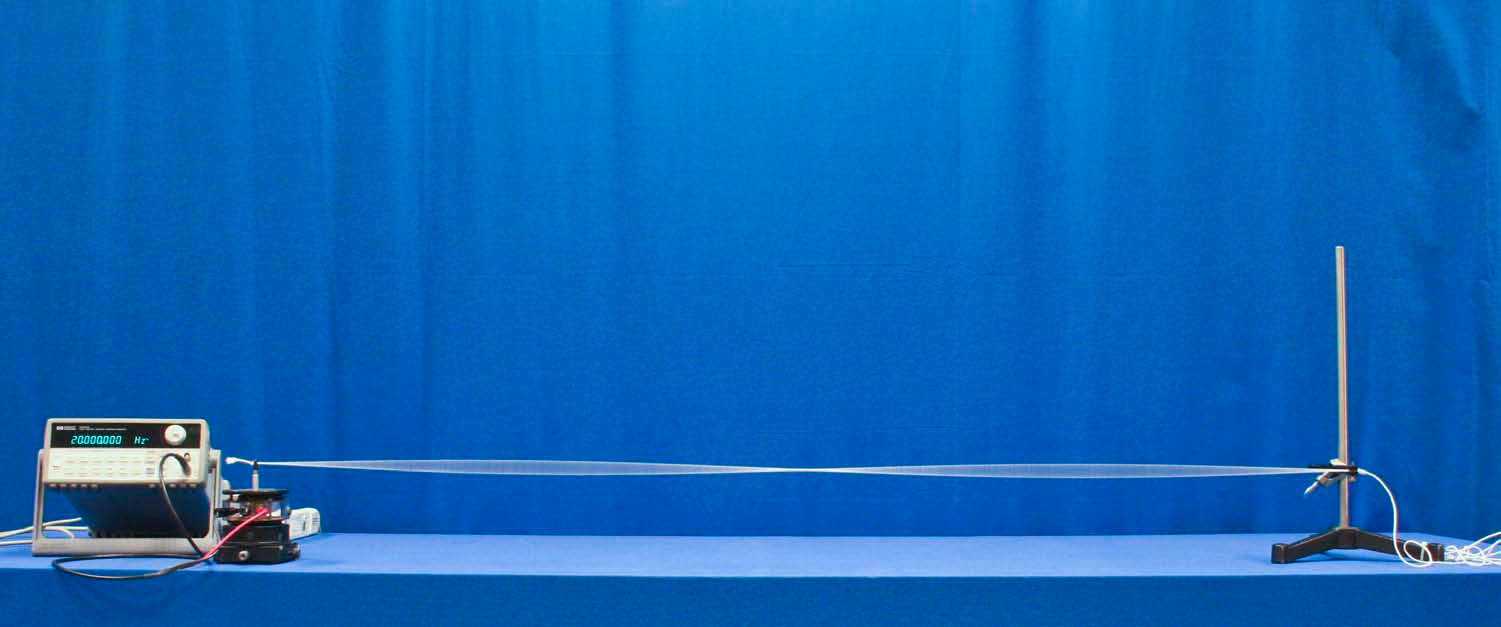
Concept
A standing wave is the superposition of traveling waves constrained between two fixed boundaries, resulting in a discrete set of modes. The wavelength of each mode $\lambda_n$ is completely determined by the distance between the fixed boundaries $L$ by the relation:
$$\lambda_n = \frac{2L}{n} $$
Thus, the frequency of each mode $(f_n)$ is:
$$ f_n = \frac{v}{\lambda_n} \text{where }v\text{ is the wave speed.}$$
Procedure
- Connect the BNC “Output” of the function generator to the banana inputs of the mechanical vibrator.
- Slot the knotted end of the cord in the vibrator pole and clamp the other end of the cord to the clamp.
- Verify that the vibrator is unlocked, turn on the function generator, and ensure the Frequency is set to 10 Hz and Amplitude is set to 6 VPP.
- If needed, adjust the tension in the elastic cord until the fundamental frequency occurs exactly at 10Hz.
- 2nd harmonic = 20 Hz, 3rd harmonic = 30 Hz, 4th harmonic = 40 Hz…
Equipment
- Function Generator (HP 33120A)
- Pasco Mechanical Vibrator
- BNC-Banana Cable
- Thin Elastic Cord
- Support Stand
- Rod Clamp
- Slotted End Clamp